Five key messages to help policymakers integrate oral health into health system responses
In the context of WHO’s recent resolution on Oral health (WHA74.5) and the upcoming 2022 Global strategy on tackling oral diseases, FDI and the NCD Alliance joined forces to develop a briefing note for policymakers.
The document calls for the integration of oral health promotion and oral healthcare into noncommunicable disease (NCD) strategies and universal health coverage (UHC) benefit packages. And it makes the case for oral health to be considered an essential element of general health and well-being.
The briefing note, which is entitled WHY and HOW to integrate oral health into the NCD and UHC responses, provides five key evidence-based messages on the associations between oral health and NCDs and the role of oral healthcare within health systems. It also provides solutions on how to implement such strategies by outlining calls to actions for each key message.
Five key messages to motivate action
- Oral health is a key indicator of general health, well-being, and quality of life, which is why oral diseases should be prioritized as part of the NCD and UHC responses. This can be supported by strong oral health information systems.
- Oral diseases and other NCDs share modifiable risk factors, and joint prevention is possible through a multisectoral response and existing cost-effective solutions.
- Poor oral health is a risk factor for NCDs, and thus health systems can be optimized and strengthened by integrating oral health promotion and oral healthcare services for all.
- Good oral health can positively impact NCD treatment outcomes so there is a need to invest in more multidisciplinary research and interprofessional collaboration across care teams.
- Engaging people living with oral diseases, communities, and health professionals is crucial to successfully integrate oral health into the NCD and UHC responses.
Why now?
In August 2021, WHO prepared the draft Global strategy on tackling oral diseases following the request made by Member States to support the implementation of the resolution on Oral health. This initial draft links oral health with NCDs by recognizing the common risk factors of oral diseases and other NCDs. However, the associations between oral health, NCDs, and general health go beyond sharing risk factors as outlined by the briefing note’s key messages.
FDI has therefore published this briefing note for policymakers, in collaboration with the NCD Alliance, and aligned with FDI’s Vision 2030: Delivering Optimal Oral Health for All and its joint response to the Global strategy calling for oral health to no longer be isolated within health systems. We must take the opportunity to improve people’s health outcomes and reduce overall health system costs by early and cost-effective oral health interventions and referrals for other NCDs.
Policymakers must build a coherent and strong 2022 Global strategy on tackling oral diseases and 2023 Action plan for public oral health, encompassing comprehensively all the implications of the associations between oral health and general health.
Snapshot of some associations between oral health and general health
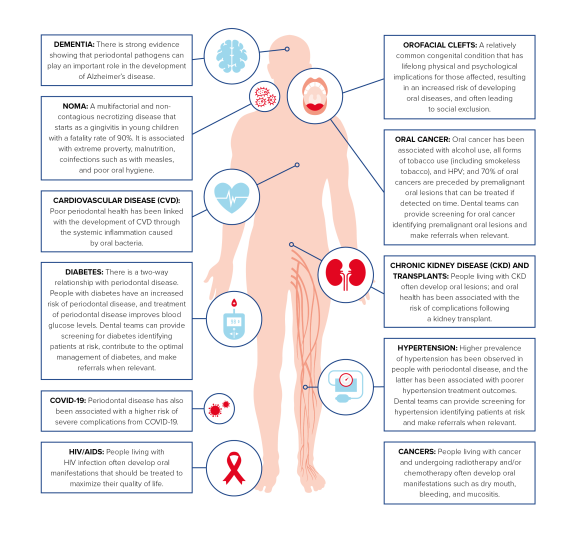
Source: FDI World Dental Federation, NCD Alliance. WHY and HOW to integrate oral health into the NCD and UHC responses. Geneva: FDI World Dental Federation; 2021.
What’s next?
We call on national dental associations (NDAs) and all health advocates to share this resource with their governments as they engage in the follow-up processes of WHO’s resolution on Oral health.
Would you like to share any feedback with us? You can contact us at advocacy@fdiworlddental.org.
